Attribute-based encryption
Synonyms: ABE
Summary
Attribute-based encryption is a type of public-key encryption in which the user's secret key and the ciphertext are dependent upon certain attributes (e.g. the country where they live or the kind of subscription they have). In such a system, the decryption of a ciphertext is only possible if the set of attributes of the user key matches the attributes of the ciphertext. The main purpose of attribute-based encryption is to implement attribute-based access control models ensured by the mathematical properties of the protocol. This approach provides better data confidentiality.
Related research paper
Our team's scientific paper on attribute-based encryption:
"Advanced attribute-based encryption protocol based on the modified secret sharing scheme".
Attribute-based encryption is a type of public-key encryption in which the user's secret key and the ciphertext are dependent upon certain attributes (e.g. the country where they live or the kind of subscription they have). In such a system, the decryption of a ciphertext is only possible if the set of attributes of the user key matches the attributes of the ciphertext. The main purpose of attribute-based encryption is to implement attribute-based access control models ensured by the mathematical properties of the protocol. This approach provides better data confidentiality.
Related research paper
Our team's scientific paper on attribute-based encryption:
"Advanced attribute-based encryption protocol based on the modified secret sharing scheme".
More on the topic
Nowadays, new technologies are developing with incredible speed. Cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), the mobile Internet have already become a regular part of our life. Amounts of data volumes are also rapidly increasing. So, how does one manage and utilize big data?
Cloud computing technology is a good tool in this regard. Cloud-based technology helps businesses get rid of all the hard work that data management requires and concentrate on their business affairs. Although cloud computing technology has many benefits, there are still many security and privacy concerns. An employee overstepping their authority or an adversary hacking into a server can compromise data confidentiality. The main protection strategy involves encrypting the data before uploading it.
Nowadays, new technologies are developing with incredible speed. Cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), the mobile Internet have already become a regular part of our life. Amounts of data volumes are also rapidly increasing. So, how does one manage and utilize big data?
Cloud computing technology is a good tool in this regard. Cloud-based technology helps businesses get rid of all the hard work that data management requires and concentrate on their business affairs. Although cloud computing technology has many benefits, there are still many security and privacy concerns. An employee overstepping their authority or an adversary hacking into a server can compromise data confidentiality. The main protection strategy involves encrypting the data before uploading it.
One can use homomorphic encryption to work with encrypted data, while attribute-based encryption (ABE) is an excellent tool for achieving flexible access control to it.
The concept of attribute-based encryption was first proposed by Amit Sahai and Brent Waters. Attribute-based encryption can be used to implement attribute-based access control models. When many users need to access information, conventional encryption schemes turn inefficient since it becomes necessary to individually re-encrypt the data with each user's public key. Attribute-based encryption schemes create a single ciphertext and control access to it depending on the access policy. Over the past few years, there have appeared protocols that provide security able to resist the potential quantum threat.
Example
Alice has attributes (A and B), and Bob has attributes (D and E). There is a document that both participants need to have access to. Instead of creating two identical files and encrypting them separately for Alice and Bob, one can create an attribute-based encrypted file with a given access policy. Only participants whose attributes satisfy the policy will be able to gain access to the file. Nowadays, there are steadily more applications using ABE for data security.
Alice has attributes (A and B), and Bob has attributes (D and E). There is a document that both participants need to have access to. Instead of creating two identical files and encrypting them separately for Alice and Bob, one can create an attribute-based encrypted file with a given access policy. Only participants whose attributes satisfy the policy will be able to gain access to the file. Nowadays, there are steadily more applications using ABE for data security.
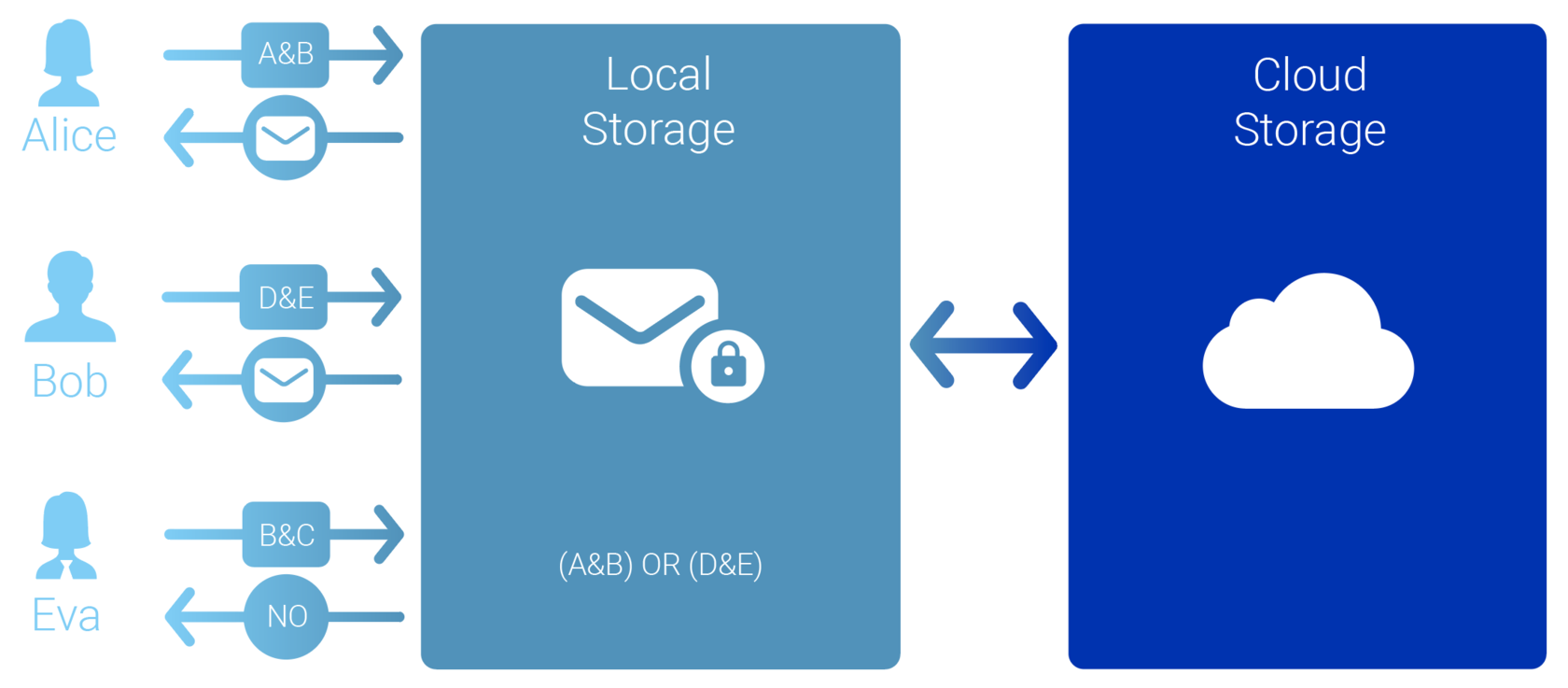
Attribute-based encryption mechanism
How to decide whether attribute-based encryption is the right choice for you?
1. Analyze the challenges to be solved in the area of providing access to sensitive information, determining the suitability of an attribute-based encryption access control model, including when the data is stored in an untrusted cloud;
2. Select and implement cryptographic algorithms optimal for solving the challenges defined in Step 1, taking the quantum threat into account;
3. Design, pilot and implement attribute-based encryption solutions together with the QApp team.
1. Analyze the challenges to be solved in the area of providing access to sensitive information, determining the suitability of an attribute-based encryption access control model, including when the data is stored in an untrusted cloud;
2. Select and implement cryptographic algorithms optimal for solving the challenges defined in Step 1, taking the quantum threat into account;
3. Design, pilot and implement attribute-based encryption solutions together with the QApp team.

